此文接上文 ,继续讲解 SparkSQL Hive ThriftServer 源码。
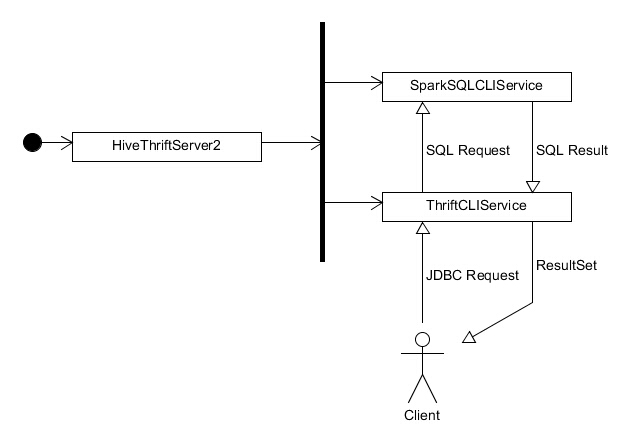
上文提到,主类 HiveThriftServer2 在启动后便会启动 ThriftCLIService 和 SparkSQLCLIService,其中 ThriftCLIService 负责维护与客户端的连接并将客户端的请求转发至 SparkSQLCLIService,由 SparkSQLCLIService 执行运算并把结果返回给 ThriftCLIService,ThriftCLIService 再把结果以 ResultSet 的形式返回给客户端。两者之间的关系如下图所示:
但当下,我们并不清楚,两个 Service 之间以及 ThriftCLIService 与客户端之间是如何完成交互的。本文将先从 SparkSQLCLIService 开始,看看在这个方向上能不能找到点线索。
SparkSQLCLIService 咱直接开始看代码吧!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 private [hive] class SparkSQLCLIService (hiveContext: HiveContext ) extends CLIService with ReflectedCompositeService { override def init HiveConf ) { setSuperField(this , "hiveConf" , hiveConf) val sparkSqlSessionManager = new SparkSQLSessionManager (hiveContext) setSuperField(this , "sessionManager" , sparkSqlSessionManager) addService(sparkSqlSessionManager) var sparkServiceUGI: UserGroupInformation = null if (ShimLoader .getHadoopShims.isSecurityEnabled) { try { HiveAuthFactory .loginFromKeytab(hiveConf) sparkServiceUGI = ShimLoader .getHadoopShims.getUGIForConf(hiveConf) HiveThriftServerShim .setServerUserName(sparkServiceUGI, this ) } catch { case e @ (_: IOException | _: LoginException ) => throw new ServiceException ("Unable to login to kerberos with given principal/keytab" , e) } } initCompositeService(hiveConf) } }
首先我们看到 SparkSQLCLISerivce 继承自 CLIService,同时混入了 ReflectedCompositeService 特质。由此可见,CompositeService 应该也是 SparkSQLCLIService 的父类之一。对比于 CLIService 的 init 方法(其部分源代码已以行注释的形式在上述对应代码中给出),SparkSQLCLIService 的 init 方法可以说完全是在做一模一样的事情,不同点仅在于 CLIService 启动一个 SessionManager,而 SparkSQLCLIService 启动了一个 SparkSQLSessionManager。我觉得光从名字上都能判断出来,SparkSQLSessionManager 一定继承自 SessionManager。
让我们继续一探究竟吧!
SparkSQLSessionManager 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 private [hive] class SparkSQLSessionManager (hiveContext: HiveContext ) extends SessionManager with ReflectedCompositeService { private lazy val sparkSqlOperationManager = new SparkSQLOperationManager (hiveContext) override def init HiveConf ) { setSuperField(this , "hiveConf" , hiveConf) val backgroundPoolSize = hiveConf.getIntVar(ConfVars .HIVE_SERVER2_ASYNC_EXEC_THREADS ) setSuperField(this , "backgroundOperationPool" , Executors .newFixedThreadPool(backgroundPoolSize)) getAncestorField[Log ](this , 3 , "LOG" ).info( s"HiveServer2: Async execution pool size $backgroundPoolSize " ) setSuperField(this , "operationManager" , sparkSqlOperationManager) addService(sparkSqlOperationManager) initCompositeService(hiveConf) } override def openSession protocol: TProtocolVersion , username: String , passwd: String , sessionConf: java.util.Map [String , String ], withImpersonation: Boolean , delegationToken: String ): SessionHandle = { hiveContext.openSession() val sessionHandle = super .openSession( protocol, username, passwd, sessionConf, withImpersonation, delegationToken) val session = super .getSession(sessionHandle) HiveThriftServer2 .listener.onSessionCreated( session.getIpAddress, sessionHandle.getSessionId.toString, session.getUsername) sessionHandle } override def closeSession SessionHandle ) { HiveThriftServer2 .listener.onSessionClosed(sessionHandle.getSessionId.toString) super .closeSession(sessionHandle) sparkSqlOperationManager.sessionToActivePool -= sessionHandle hiveContext.detachSession() } }
果不其然,SparkSQLSessionManager 的 init 方法与 SessionManager 的 init 方法极为相似。从名字上看,Session Manager 当然是用来管理 Session 的了。SparkSQLSessionManager 的 openSession 和 closeSession 方法都有调用 SessionManager 的对应方法来管理 HiveSession,同时还管理了 HiveContext 内部的 SQLSession。简单的查看 HiveSession 和 SQLSession 的定义,可以得出结论,HiveSession 指的是 Hive ThriftServer 与 Client 之间的 Session,即通常意义上的网络 Session;而 SQLSession 指的是 SparkSQL 与 Hive ThriftServer 之间的 Session,但 SQLSession 实际存储的只是一系列与 SQL 查询有关的配置参数,和传统意义上的网络 Session 不同。
SparkSQLSessionManager 与 SessionManager 的不同点在于 SparkSQLSessionManager 启动了一个 SparkSQLOperationManager,而 SessionManager 启动的是 OperationManager。那么,其实也能猜到一些了。
SparkSQLOperationManager 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 private [thriftserver] class SparkSQLOperationManager (hiveContext: HiveContext ) extends OperationManager with Logging { val handleToOperation = ReflectionUtils .getSuperField[JMap [OperationHandle , Operation ]](this , "handleToOperation" ) val sessionToActivePool = Map [SessionHandle , String ]() override def newExecuteStatementOperation parentSession: HiveSession , statement: String , confOverlay: JMap [String , String ], async: Boolean ): ExecuteStatementOperation = synchronized { val operation = new SparkExecuteStatementOperation (parentSession, statement, confOverlay)( hiveContext, sessionToActivePool) handleToOperation.put(operation.getHandle, operation) operation } }
简短,直白。很明显,newExecuteStatementOperation 方法会在客户端发送 JDBC 请求后被调用。方法创建了一个 SparkExecuteStatementOperation,并将其进行缓存管理。实际上,SparkSQLOperationManager 只复写了 OperationManager 的 newExecuteStatementOperation 方法,除此之外 OperationManager 还有 newGetSchemasOperation 等其他方法。这些方法从命名上判断,都是用户在查询表的元数据时才会触发的操作,比如 newGetSchemasOperation 应该是会在用户试图查询某张表的模式的时候才会触发的操作。SparkSQL 之所以要重载 newExecuteStatementOperation 的原因是显然的:Execute 意味着执行,SparkSQL Hive ThriftServer 通过重载该方法,把用户通过 execQuery 发送的执行请求转发至 SparkSQL。
那就直接看看 SparkExecuteStatementOperation 到底干了什么吧(如果你已经猜到了,我并不会觉得意外 ;-) )。
SparkExecuteStatementOperation 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 private [hive] class SparkExecuteStatementOperation ( parentSession: HiveSession , statement: String , confOverlay: JMap [String , String ], runInBackground: Boolean = true )( hiveContext: HiveContext , sessionToActivePool: SMap [SessionHandle , String ] ) extends ExecuteStatementOperation (parentSession, statement, confOverlay, false ) with Logging { private var result: DataFrame = _ private var iter: Iterator [SparkRow ] = _ private var dataTypes: Array [DataType ] = _ def close Unit = { logDebug("CLOSING" ) } def getNextRowSet FetchOrientation , maxRowsL: Long ): RowSet = { } def getResultSetSchema TableSchema = { } def run Unit = { val statementId = UUID .randomUUID().toString logInfo(s"Running query '$statement '" ) setState(OperationState .RUNNING ) HiveThriftServer2 .listener.onStatementStart( statementId, parentSession.getSessionHandle.getSessionId.toString, statement, statementId, parentSession.getUsername) hiveContext.sparkContext.setJobGroup(statementId, statement) sessionToActivePool.get(parentSession.getSessionHandle).foreach { pool => hiveContext.sparkContext.setLocalProperty("spark.scheduler.pool" , pool) } try { result = hiveContext.sql(statement) logDebug(result.queryExecution.toString()) result.queryExecution.logical match { case SetCommand (Some ((SQLConf .THRIFTSERVER_POOL , Some (value))), _) => sessionToActivePool(parentSession.getSessionHandle) = value logInfo(s"Setting spark.scheduler.pool=$value for future statements in this session." ) case _ => } HiveThriftServer2 .listener.onStatementParsed(statementId, result.queryExecution.toString()) iter = { val useIncrementalCollect = hiveContext.getConf("spark.sql.thriftServer.incrementalCollect" , "false" ).toBoolean if (useIncrementalCollect) { result.rdd.toLocalIterator } else { result.collect().iterator } } dataTypes = result.queryExecution.analyzed.output.map(_.dataType).toArray setHasResultSet(true ) } catch { case e: Throwable => setState(OperationState .ERROR ) HiveThriftServer2 .listener.onStatementError( statementId, e.getMessage, e.getStackTraceString) logError("Error executing query:" , e) throw new HiveSQLException (e.toString) } setState(OperationState .FINISHED ) HiveThriftServer2 .listener.onStatementFinish(statementId) } }
那其实就很一目了然了:用户通过 JDBC execQuery 发送的请求最终被原封不动地转发到了 HiveContext.sql 上进行运算,结果保存在 SparkExecuteStatementOperation 中,同时保存一个 Iterator,视客户端所需逐行逐行地以 ResultSet 的形式取出,并返回至客户端。
至此,SparkSQLCLIService 一侧的运作原理就基本探索完毕了。
总结 在深入了解过 SparkSQLCLIService 一侧的原理以后,之前那张图大概就会变成下面这个样子:
总体而言,Spark Hive ThriftServer 确实是基于 Apache Hive 的基础之上通过少量的修改、继承甚至是利用 Java 反射机制来 hack Hive 原本的类来将 Hive 本该转发至 Hadoop MapReduce 的操作转发到了 SparkSQL 的 HiveContext.sql,因此在 JDBC 上调用 execQuery 和直接调用 HiveContext.sql 的效果是一致的。
除了 SparkSQLCLISerivce,ThriftCLIService 侧的代码其实都是 Apache Hive 本身的代码,Spark 未对其进行任何改写。Spark Hive ThriftServer 项目本身的所有代码仅包括 SparkSQLCLIService 这一侧的代码和 Spark SQL Shell 的代码。因此总体而言,在阅读完本篇文章后,你应该已经完全了解 Spark Hive ThriftServer 的工作原理了。Hive ThriftCLIService 一侧的代码很有可能我不会再去看了,因为那一侧的代码的功能已经十分明确,但由于涉及到网络通信,毫无疑问那一侧的代码量将会是这一侧的好几倍。因此如果你只是想了解 SparkSQL Hive Server 的运作原理,你的目的已经达到了。恭喜你!